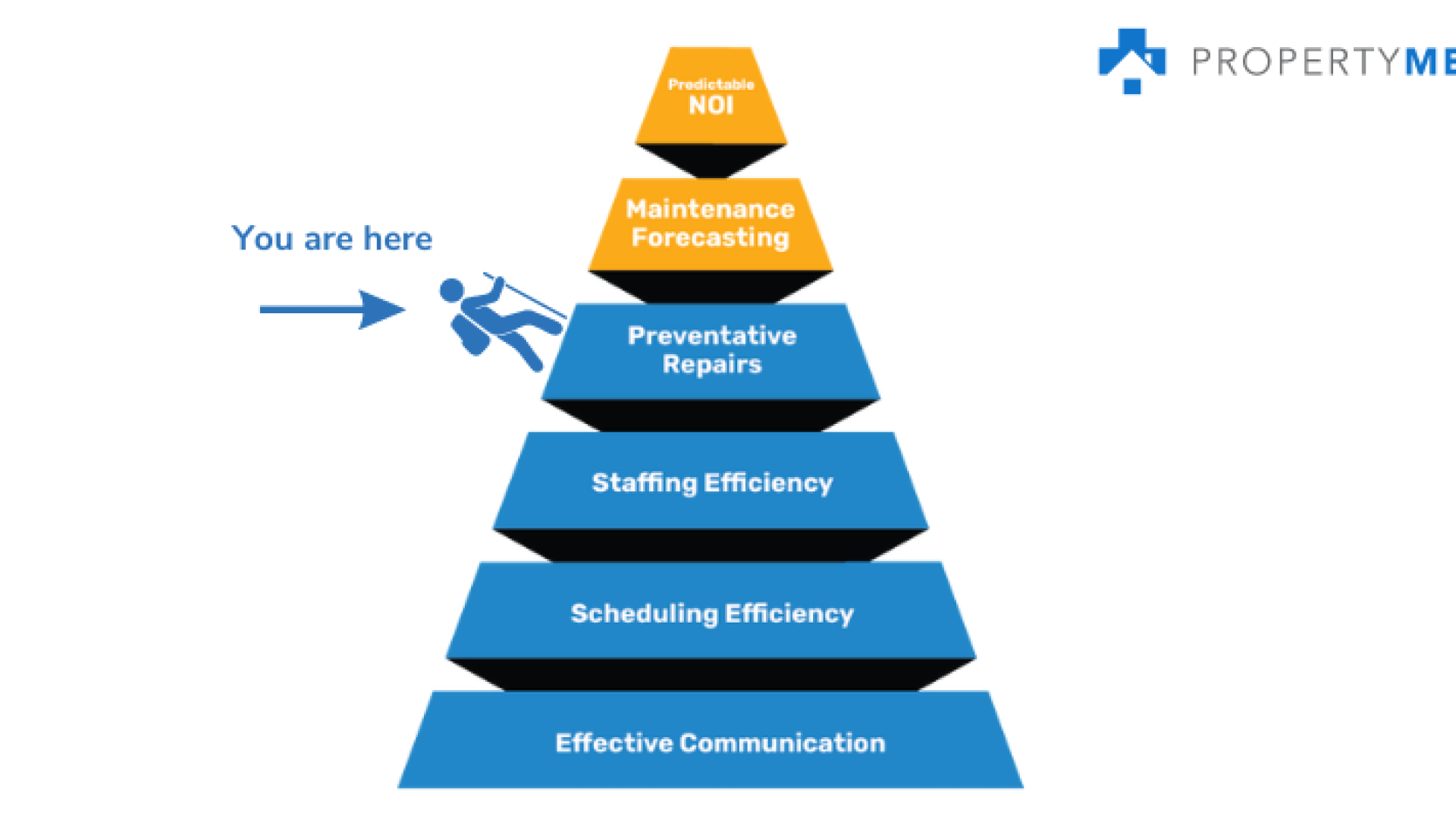
What is Preventative Maintenance?
In property maintenance, preventative maintenance refers to the proactive and scheduled maintenance activities carried out to prevent property-related issues and ensure the proper functioning and longevity of the property and its appliances. It involves inspecting, cleaning, and maintaining various systems, structures, and equipment within a property with the primary objective of identifying and rectifying potential concerns before they escalate into significant challenges.
However, if you still need to solve communication, scheduling efficiency, and staffing issues, handling preventative repairs may be challenging. To learn more about solving these things and achieving maintenance excellence, subscribe to The Maintenance Minute.
Examples of preventative maintenance tasks in property maintenance include:
1. HVAC System Maintenance: Regularly cleaning and servicing heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to ensure optimal performance and prevent breakdowns.
2. Plumbing Maintenance: Inspecting and maintaining plumbing fixtures, pipes, and drains to prevent leaks, clogs, and water damage.
3. Electrical System Maintenance: Checking electrical wiring, outlets, and panels for any signs of wear or malfunctioning to minimize the risk of electrical failures or hazards.
Why is Preventative Maintenance Important?
Preventative maintenance for properties is important for several reasons:
- Cost Savings: Implementing a proactive maintenance approach can help property management companies save their owners money in the long run. By identifying and addressing minor issues before they escalate into major problems, preventative maintenance can prevent costly repairs or replacements. It is generally more cost-effective to perform regular maintenance tasks than to deal with large-scale repairs or emergency fixes.
- Increased Lifespan of Property: Regular maintenance helps prolong the lifespan of various property components, such as HVAC systems, plumbing systems, roofs, and equipment. By keeping them in good working condition, properties can function optimally and remain in good shape for a longer period, reducing the need for premature replacements.
- Minimized Downtime and Disruptions: Unplanned breakdowns or failures of critical systems can lead to significant downtime and disruptions in property operations.
- Enhanced Safety: Regular inspections and maintenance activities ensure that safety hazards are identified and addressed promptly. Faulty electrical systems, leaking pipes, damaged flooring, or unsafe structures can pose risks to occupants or visitors. Preventative maintenance helps mitigate these risks, creating a safer environment for everyone.
Overall, preventative maintenance for properties is crucial for cost savings, property preservation, safety, and uninterrupted operations. It provides peace of mind to property owners and residents, reduces risks, and contributes to the long-term success of the property.
What Metrics are Involved in Preventative maintenance?
When tracking preventative property maintenance, several metrics can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and efficiency of the maintenance program. Here are some key metrics that should be tracked:
- Maintenance Costs: Monitoring the costs associated with preventative maintenance activities provides an overview of the financial investment required to keep the property in good condition. This includes expenses such as labor, materials, equipment, and external service providers. Analyzing maintenance costs over time can help identify trends, cost-saving opportunities, and areas where maintenance efforts may need adjustment.
- Asset Downtime: Tracking asset downtime helps measure the effectiveness of preventative maintenance in minimizing disruptions. This metric measures the amount of time assets or systems are non-functional due to maintenance activities. A reduction in asset downtime indicates successful maintenance efforts in preventing unexpected failures or breakdowns.
- Work Order Completion Time: This metric measures the time it takes to complete maintenance work orders from the moment they are initiated. Tracking work order completion time helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, or delays in the maintenance process. It allows for better planning, resource allocation, and streamlining of maintenance tasks.
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): MTBF calculates the average time between failures of a particular asset or system. By tracking MTBF, property owners can assess the effectiveness of preventative maintenance in increasing the reliability and lifespan of assets. A higher MTBF indicates longer periods of uninterrupted operation and successful maintenance efforts.
- Resident Satisfaction: Resident satisfaction surveys or feedback can provide valuable insights into the impact of preventative maintenance on resident experience. Tracking resident satisfaction helps gauge how well the maintenance efforts are meeting the needs and expectations of the property’s occupants. Higher satisfaction levels indicate successful maintenance practices and a well-maintained property.
These metrics, when analyzed regularly, can help property managers make data-driven decisions, identify areas for improvement, optimize maintenance strategies, and ensure the effectiveness of preventative property maintenance programs. To learn more about understanding maintenance metrics and how they are used, check out this article.
Request a demo with our team if you are interested in learning more about preventative maintenance and how it can be automated with our platform.